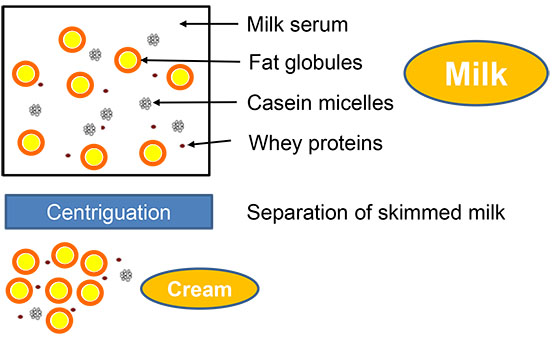
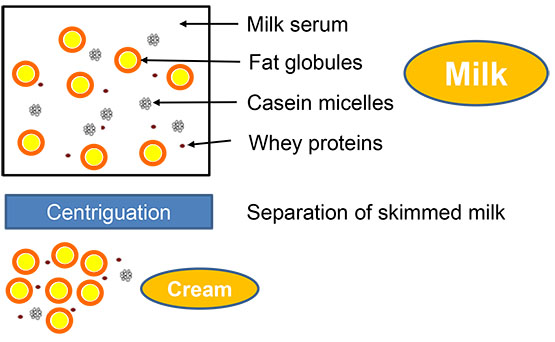
Cream is the fat-rich fraction of milk that is extracted by an appropriate process, e.g. centrifugation, and has the same phase distribution as milk (oil in water) (cf. figure).
1. Definitions
Cream obtained from whey must be described as whey cream. A blend of whey cream and cream must be labelled as cheesemaking cream or whey cream.
2. Description
The fat content of cream varies according to its intended use, the upper limit being approx. 800 g/kg for technological reasons.
Cream for the retail trade is generally pasteurised or undergoes UHT (ultra-high temperature) processing, and may contain up to 30 g additional milk components per kilogram as well as additives in conformity with the Additives Ordinance, e.g. thickeners, emulsifying agents and stabilisers in whipping cream. With regard to prevention of the addition of water, the same requirements apply to cream as to milk. There must therefore be at least 85 g/kg of ‘fat-free dry matter’ in the fat-free fraction (serum), i.e. for a cream with a fat content of 350 g/kg cream, the fat-free dry matter must be at least 55.25 g/kg cream.
The fat-free dry matter in whole cream (which contains 35% fat according to Swiss legislation) is usually around 58 to 62 g/kg cream. In a number of European countries whole cream contains 30% fat.
Depending on the product, it may be even higher if milk-protein concentrates have been added.
3. Classification by Fat-Content Stage (Swiss Legislation)
Cream is classified according to fat content levels in accordance with the Swiss Ordinance on foodstuffs of animal origin as described in the following table (as at May 2016).
Fat Content in g/kg |
Name |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
≥ 150 |
Half cream or Coffee cream |
Whippable half cream often has a fat content of 25%. |
≥ 350 |
Full cream, Whipping cream, Cream |
Pasteurised: Limited authorisation of thickeners and emulsifying agents Other cream products: more additives allowed. |
≥ 450 |
Double cream |
Example: Crème de Gruyère |
|
Thickened cream |
Cream that has become thick-to be-spreadable through the addition of thickeners |
|
Cultured cream, including crème fraîche |
Fermented with suitable microorganisms, generally mesophilic lactococci and Leuconostoc, with the creation of flavour compounds, in particular diacetyl. |
4. Mean Chemical Composition of Cream
The chemical characterisation is subdivided into major, minor and trace components. Average values for the most important products available on the Swiss market are listed in Tables 1 and 2 (Agroscope data).
| Contents | Full Cream | Half Cream UHT | Half Cream PAST | Coffee Cream |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat | 349-351 | 247-255 | 266-292 | 147-153 |
| Dry matter | 305-410 | 319-325 | 333-351 | 222-228 |
| Water | 590-595 | 675-681 | 649-667 | 772-778 |
| Fat-free DM* | 55-60 | 69-75 | 67-75 | 70-78 |
| Protein | 19-21 | 25-27 | 22-24 | 26-28 |
| Lactose | 30-32 | 36-38 | 31-35 | 36-40 |
| Ash | 4.3-4.7 | 5.6-6.0 | 5.0-5.3 | 6.2-7.2 |
| Cholesterol | 0.91-1.11 | 0.72-0.92 | 0.65-0.77 | 0.49-0.51 |
| Sodium* | 0.24-0.26 | 0.21-0.47 | 0.32-0.38 | 0.55-1.01 |
| Calcium | 0.4-0.8 | 0.8-0.85 | 0.75-0.81 | 0.89-0.93 |
| Potassium | 1.0-1.3 | 1.35-1.6 | 1.2-1.5 | 1.36-1.46 |
| Magnesium | 0.06-0.065 | 0.08-0.09 | 0.05-0.09 | 0.074-0.083 |
| Phosphorus | 0.5-0.9 | 0.7-0.77 | 0.55-0.7 | 0.77-1.05 |
| Contents | Full Cream | Half Cream UHT | Half Cream PAST | Coffee Cream |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | 0.43-0.83 | 0.35-0.65 | 0.22-0.45 | 0.15-0.45 |
| Copper | 0.025-0.051 | 0.025-0.043 | 0.022-0.042 | 0.015-0.041 |
| Vitamin A | 3.7 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 1.4 |
| Vitamin E | 8.0 | 6.9 | 6.2 | 3.4 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.2 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.17 |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.21 |
Sieber R., Badertscher R., Eyer H., Fuchs D., Nick B., 1996. Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Zusammensetzung von schweizerischem Voll-, Halb- und Kaffeerahm. Mitt. Gebiete Lebensm. Hyg. 87, 103-110, 653.